External tools
Post-processing for charge density, band density, DOS, STM
The utility PostProcessCQ allows users to post-process the output
of a CONQUEST calculation, to produce the charge density, band
densities, DOS and STM images in useful forms. It is described fully here.
Molecular dynamics analysis
Several scripts that may be helpful with postprocessing molecular dynamics are
included with CONQUEST. The can be found in the tools directory, and the
executables are plot_stats.py, md_analysis.py and heat_flux.py. They
have the following dependencies:
Python 3
Scipy/Numpy
Matplotlib
If Python 3 is installed the modules can be added easily using pip3 install
scipy etc.
These scripts should be run in the calculation directory, and will automatically
parse the necessary files, namely Conquest_input, input.log,
md.stats and md.frames assuming they have the default names. They will
also read the CONQUEST input flags to determine, for example, what ensemble is
used, and process the results accordingly.
Go to top.
Plotting statistics
usage: plot_stats.py [-h] [-c] [-d DIRS [DIRS ...]]
[--description DESC [DESC ...]] [--skip NSKIP]
[--stop NSTOP] [--equil NEQUIL] [--landscape]
[--mser MSER_VAR]
Plot statistics for a CONQUEST MD trajectory
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c, --compare Compare statistics of trajectories in directories
specified by -d (default: False)
-d DIRS [DIRS ...], --dirs DIRS [DIRS ...]
Directories to compare (default: .)
--description DESC [DESC ...]
Description of graph for legend (only if using
--compare) (default: )
--skip NSKIP Number of equilibration steps to skip (default: 0)
--stop NSTOP Number of last frame in analysis (default: -1)
--equil NEQUIL Number of equilibration steps (default: 0)
--landscape Generate plot with landscape orientation (default:
False)
--mser MSER_VAR Compute MSER for the given property (default: None)
Running plot_stats.py --skip 200 in your calculation will generate a plot
which should resemble the example below, skipping the first 200 steps. This
example is a molecular dynamics simulation of 1000 atoms of bulk silicon in the
NPT ensemble, at 300 K and 0.1 GPa.
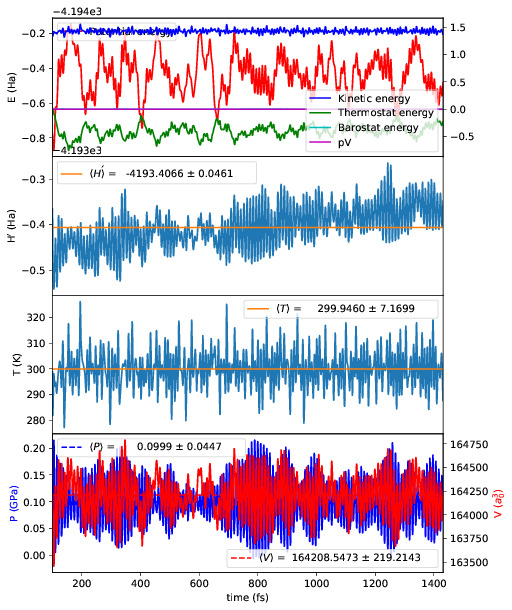
The four plots are respectively the breakdown of energy contributions, the
conserved quantity, the temperature and the pressure, the last of which is only
included for NPT molecular dynamics. Several calculations in different
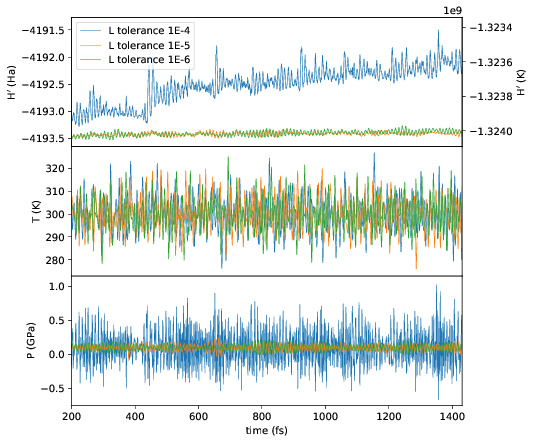
directories can be compared using plot_stats.py --compare -d dir1
dir2 --description "dir1 description" "dir2 description". The following
example compares the effect of changing the L tolerance in the above simulation.
Note that the contents of the description field will be in the legend of the
plot.
Go to top.
MD analysis
usage: md_analysis.py [-h] [-d DIRS [DIRS ...]] [--skip NSKIP]
[--stride STRIDE] [--snap SNAP] [--stop NSTOP]
[--equil NEQUIL] [--vacf] [--msd] [--rdf] [--stress]
[--nbins NBINS] [--rdfwidth RDFWIDTH] [--rdfcut RDFCUT]
[--window WINDOW] [--fitstart FITSTART] [--dump]
Analyse a CONQUEST MD trajectory
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d DIRS [DIRS ...], --dirs DIRS [DIRS ...]
Directories to compare (default: .)
--skip NSKIP Number of equilibration steps to skip (default: 0)
--stride STRIDE Only analyse every nth step of frames file (default:
1)
--snap SNAP Analyse Frame of a single snapshot (default: -1)
--stop NSTOP Number of last frame in analysis (default: -1)
--equil NEQUIL Number of equilibration steps (default: 0)
--vacf Plot velocity autocorrelation function (default:
False)
--msd Plot mean squared deviation (default: False)
--rdf Plot radial distribution function (default: False)
--stress Plot stress (default: False)
--nbins NBINS Number of histogram bins (default: 100)
--rdfwidth RDFWIDTH RDF histogram bin width (A) (default: 0.05)
--rdfcut RDFCUT Distance cutoff for RDF in Angstrom (default: 8.0)
--window WINDOW Window for autocorrelation functions in fs (default:
1000.0)
--fitstart FITSTART Start time for curve fit (default: -1.0)
--dump Dump secondary data used to generate plots (default:
False)
The script md_analysis.py script performs various analyses of the trajectory
by parsing the md.frames` file. So far, these include the radial distribution
function, the velocity autocorrelation function, the mean squared deviation, and
plotting the stress. For example, the command,
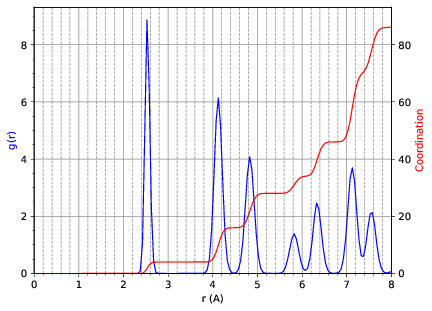
md_analysis.py --rdf --stride 20 --rdfcut 8.0 --nbins 100 --dump --skip 200 --stop 400
computes the radial distribution function of the simulation in the first example from every 20th time step (every 10 fs in this case), stopping after 400 steps, with a cutoff of 8.0 A, and the histogram is divided into 100 bins.
Go to top.
CONQUEST structure file analysis
usage: structure.py [-h] [-i INFILE] [--bonds] [--density] [--nbins NBINS]
[-c CUTOFF [CUTOFF ...]] [--printall]
Analyse a CONQUEST-formatted structure
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INFILE, --infile INFILE
CONQUEST format structure file (default:
coord_next.dat)
--bonds Compute average and minimum bond lengths (default:
False)
--density Compute density (default: False)
--nbins NBINS Number of histogram bins (default: 100)
-c CUTOFF [CUTOFF ...], --cutoff CUTOFF [CUTOFF ...]
Bond length cutoff matrix (upper triangular part, in
rows (default: None)
--printall Print all bond lengths (default: False)
The script structure.py can be used to analyse a CONQUEST-formatted
structure file. This is useful to sanity-check the bond lengths or density,
since an unphysical structure is so often the cause of a crash. For example, the
bond lengths can be computed with
structure.py --bonds -c 2.0 3.0 3.0
where the -c flag specifies the bond cutoffs for the bonds 1-1, 1-2 and 2-2,
where 1 is species 1 as specified in Conquest_input and 2 is species 2. The
output will look something like this:
Mean bond lengths:
O-Si: 1.6535 +/- 0.0041 (24 bonds)
Minimum bond lengths:
O-Si: 1.6493
Go to top.
Atomic Simulation Environment (ASE)
ASE is a set of
Python tools for setting up, manipulating, running, visualizing and analyzing
atomistic simulations. ASE contains a CONQUEST interface, also
called Calculator so that it can be used to calculate energies, forces
and stresses as inputs to other calculations such as Phonon
or NEB that
are not implemented in CONQUEST. ASE is a versatil tool to manage CONQUEST
calculations without pain either:
in a direct way where pre-processing, calculation and post-processing are managed on-the-fly by ASE,
or in an indirect way where the calculation step is performed outside the workflow, ie. on a supercomputer.
The ASE repository containing the Conquest calculator can be found here. Detailed documentation on how to manage Conquest calculations with ASE is available here.
Go to top.